For this blog we are unpacking What are By-products and How to Manage Them?
By-products are secondary products produced when manufacturing another product.
Examples include:
- Honey used as a component in a primary product. The left over honey frozen and reused in another product
- Sheet metal is cut for a primary product. The scraps are used for smaller primary products
By-products are defined on the Bill of Materials with a component type of By-product.
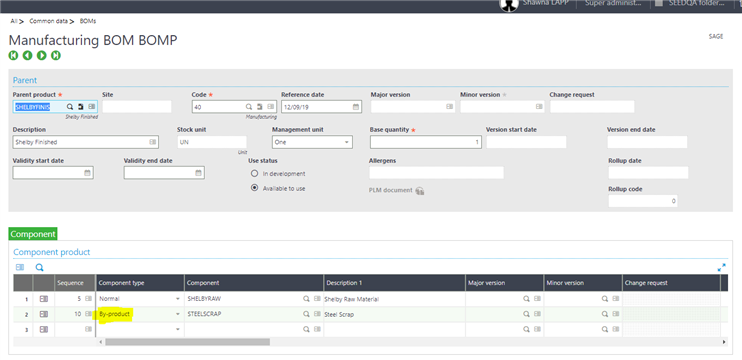
When the Valuation = "yes" then the value of the by-product is taken into account when calculating the standard cost of the product.
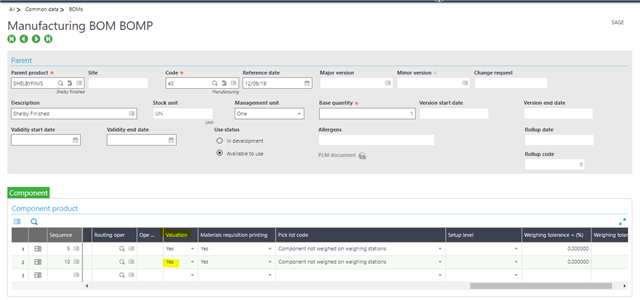
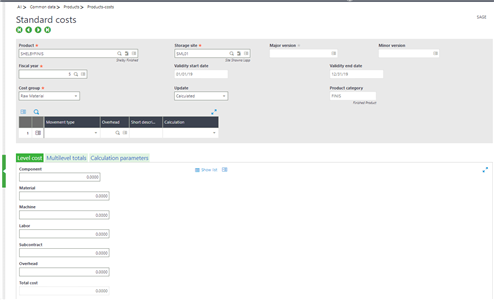
The calculated standard cost will be reduced by the value of the By-product when Valuation = "yes"
When the work order is created for the finished product, the By-product will appear
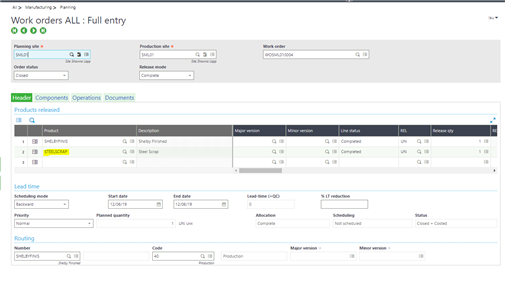
What happens when a By-product is processing?
- MRP a suggested By-product working record is created for the By-product and increasing the stock record.
- Work Orders, a firm By-product record is created for the By-product.
- Production tracking, it is tracked with the manufactured product.
- Obtener enlace
- X
- Correo electrónico
- Otras aplicaciones
- Obtener enlace
- X
- Correo electrónico
- Otras aplicaciones